Field Where Dangerous Gases Generate
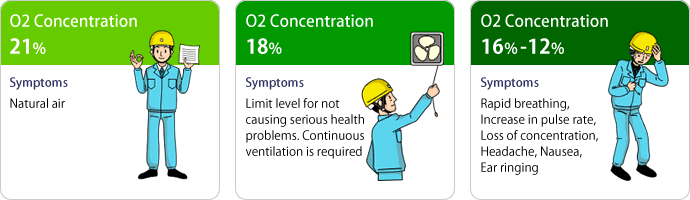
How Human Body React to Oxygen Deficiency

Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) on Human Body
%20on%20Hum.jpg)
Effect of Carbon Monoxide (CO) on Human Body
%20on%20Human.jpg)
Properties and Dangers of Flammable Gases (Isobutane: i-C4H10)

Properties and Dangers of Flammable Gases (Methane: CH4)

Tanks and Manholes
Manholes, stormwater pits and raw water tanks at sewage treatment plants can easily cause oxygen deficiency and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) poisoning from decomposing organic matter.
There is a high possibility of encountering drowning accidents that workers faint and fall into the confined spaces as a consequence of one breath of oxygen lacked air or highly concentrated hydrogen sulfide (H2S).

Sewers
Sediment in sewers contain many kinds of components such as sulfuric acid and sodium sulfide from treatment plants as well as amino acids from food processing plants.
It is easy for sulfuric acid and sodium sulfide to produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S). In addition, the characteristic of these gases to breath oxygen in air also induces an oxygen deficiency.

Ballast Tanks and Cargo Tanks in Ships
Ballast tanks take in and expel water to maintain a ship's balance. The steel plating on the walls inside become oxidized with surprising speed.
In the cargo tanks, massive amounts of oxygen are consumed by processes such as the respiration activity of fruits and grains or vaporizing dry ice used for the refrigeration.

Garbage Disposal Facilities
The incinerator ash contains sulfides produced when the sulfurous compounds inside garbage are incinerated. These sulfides become sources to generate hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and to decrease in oxygen (O2) levels in air.

List of Toxic Gas to be Detected

List of Combustible Gas to be Detected


